Why Protein is the Key to Successful Dieting
When we talk about protein, it is usually in the context of building muscle. Yet there is another side to the protein body transformation equation - weight loss. In this article, I will shed light on how and why you should prioritize protein in your quest to lose body fat.
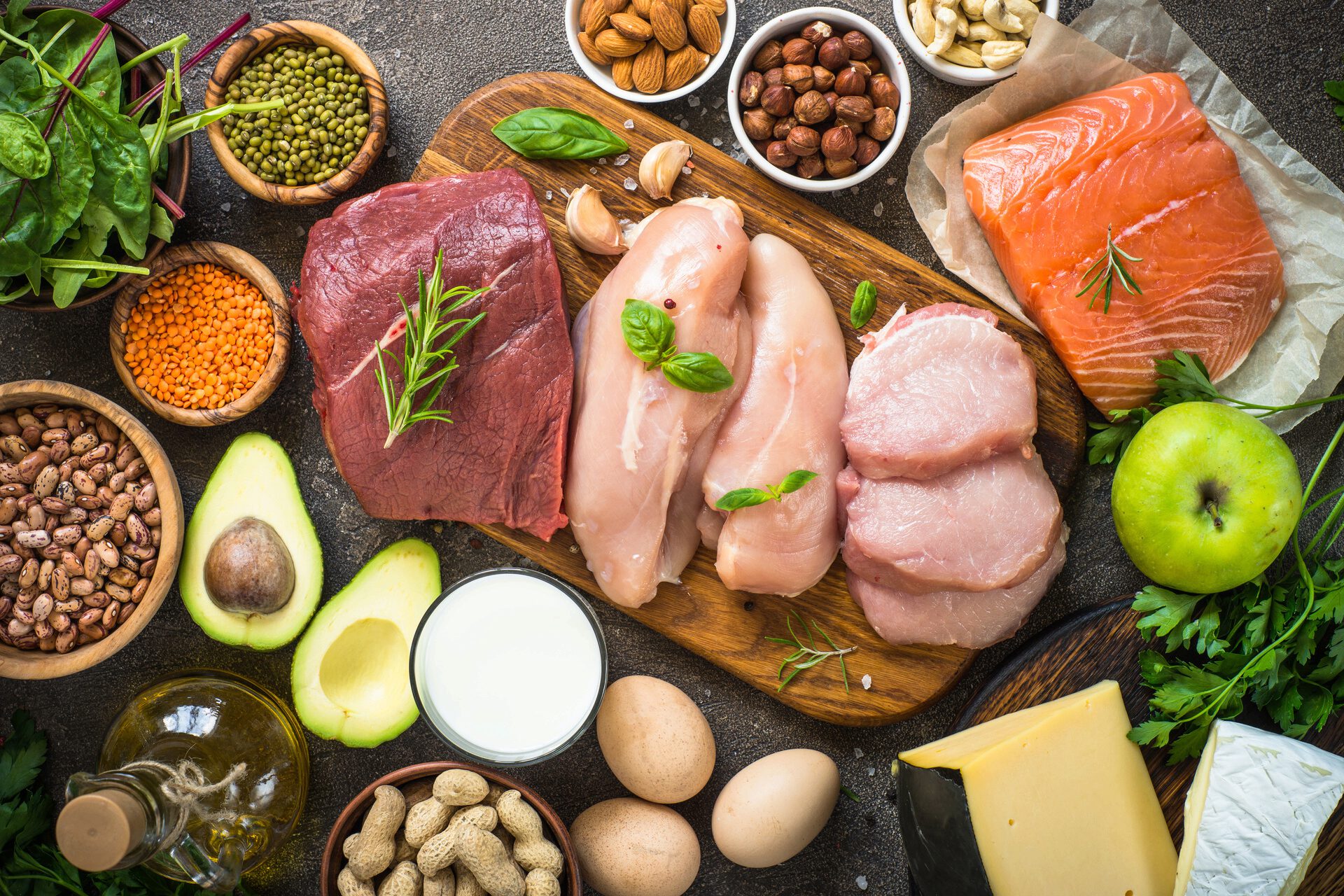
Protein is one of the three key macronutrients in your body, along with fats and carbohydrates. The ancient Greeks considered it to be the number one nutrient and so gave it the name proteios, which translates as ‘most important’.
The key constituents of protein are amino acids. These are the building blocks of your body that make up everything from your toenails to your eyelids.
There are 20 amino acids that combine in all sorts of configurations to create the different parts of your body. Your body is able to create 11 of those amino acids. The other nine need to come from your diet. These are called the essential amino acids.
Here’s a list of those nine essential amino acids:
- Histidine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Lysine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Valine
Protein promotes weight loss in three important ways:
- It forms the building material of muscle. The more muscle you have on your body, the more energy the body needs to produce to keep you functioning. As a result, your metabolism increases so that you are burning more calories at rest.
- Protein has the highest thermic value of the three macronutrients. That means that it takes more energy in the form of calories to digest protein food than it does a carbohydrate or a fat food. Between 25 and 30% of the calories that are in a protein will be consumed in the act of digestion. This compares to just 6 to 8% for carbohydrates and 2 to 3% for fat.
- Protein is the most satiating of the three macronutrients. That means that it will fill you up faster than carbs or fats. As a result, if you build your meals around a quality source of lean protein, you will be far less likely to snap between meals or to be tempted by sugary carb foods when you pass by a bakery.
There is an impressive body of research showing that these key weight loss benefits of protein combine to speed up weight loss. Study after study shows that when these components are divided into three groups, each one eating more of a particular macronutrient, it is always the high-protein group that loses the most weight, builds the most lean muscle tissue, is less hungry and consumes fewer total calories each day.
In contrast, study participants who reduce their protein intake are far more prone to consuming more calories, gaining excess body fat and losing lean muscle tissue. Studies like these have led some researchers to a belief in what is called the protein leverage hypothesis.
According to this theory, human beings have an innate ability to track the amount of protein they are consuming. It is believed that this tracking system is what controls our appetite. When we are lacking in protein, we eat more and when we are meeting our protein needs, eat less.
The protein leverage hypothesis provides an answer to the question of why poorer people are invariably more overweight than more wealthy people. Protein is by far the most expensive of the three macronutrients. Poorer people are far more likely to eat cheap processed carbohydrates and fats than quality lean proteins. In contrast, the wealthy are more likely to consume quality lean proteins such as fish, steak and chicken on a daily basis.
As previously mentioned, there are nine essential amino acids that we need to get from foods we eat. When it comes to building muscle, these nine are not all equal. There are three of them that are more important than the others. These are known as the branch chain amino acids. They are:
- Valine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
Of the three, leucine is the most important of all. Even though your goal is to lose body fat rather than gain a lot of muscle, we can only ignore the fact that every ounce of muscle on your body is going to make you a far more efficient fat burner. It takes five times more energy to sustain a pound of muscle as it does a pound of fat. That’s five times the rate of calorie burn every second of the day, 24-hours a day!
The process by which amino acids build muscle tissue is called muscle protein synthesis. This is maximized when you have about 1.5 g of leucine in your muscle tissue. The best foods to consume to make that happen are:
- Chicken breast
- Whey protein powder
- Cottage cheese
- Soybeans
Eggs are another excellent source of protein, along with healthy fats. A single egg will provide you with 6 grams of protein. Egg protein is also the most bioavailable, meaning that nearly all of it will be used by the body.
I recommend getting into the habit of having hard-boiled eggs available as a quick and easy snack when you are feeling peckish. A single egg will take away your hunger pangs, keeping you satisfied until your next scheduled meal.
A workout program that will help your muscle grow with all this protein consumed:
There has been a load of debate about the ideal amount of protein in the diet. The consensus among researchers is that around 30% of your total calories each day come from protein. That works out to 600 calories per day from protein on a 2000 calorie diet.
There are four grams of protein in every calorie. So, we can work out how many grams of protein we should be eating on a 2000 calorie daily diet … 600 divided by 4 = 150 grams of protein
You should spread your protein consumption over the course of the day. So, if you are having six meals a day, which we recommend, (3 main meals and two snacks), you should be getting around 30 grams per meal.
Protein should form the basis of your weight loss nutrition plan. By eating a good amount of lean protein at each meal, you will be far less likely to succumb to the sugary carbs that will play havoc with your insulin and blood sugar levels.
Plan to eat 30% of your calories from protein each day, spread over 3 main and 2 snack meals. As an easy guide, have a protein portion the size of your fist at main meals and the size of your two thumbs at snack meals.