What Is Ozempic and Is It Really Safe for Weight Loss?
The perception of weight management and obesity is finally evolving. What was once a conversation centered around blame and personal failure is now shifting towards finding effective solutions that not only address unwanted weight but also improve overall health and fitness.
Around the world, more people are seeking alternative methods to manage their weight, recognizing that traditional diet and exercise may not always be enough. Medications are becoming a popular option, and one drug that has been gaining significant attention is Ozempic.
Initially developed to help manage type 2 diabetes, Ozempic is now being used for its potential to aid in weight loss, making waves in the U.S., Europe, and Asia as a promising tool in managing the obesity epidemic.
But as with any medication, it's important to ask: Is Ozempic safe? Is it suitable for everyone? How should it be used effectively, especially for those combining it with a fitness regimen?
In this article, we'll take a closer look at Ozempic—its function, safety, and effectiveness for weight loss and how it fits into a balanced fitness plan.
Ozempic is a prescription medication originally created to help people with type 2 diabetes manage their blood sugar levels. However, medical researchers have recently discovered that it can also help with weight loss.
The key ingredient in Ozempic is called semaglutide, which works by mimicking a natural hormone called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) in your body that helps regulate hunger.
It reduces appetite and makes you feel fuller for longer, so you end up eating less without feeling deprived. It also slows down how quickly food leaves your stomach, which can help you stay satisfied between meals.
These processes lead to a caloric deficit, which is essential for weight loss. Patients taking Ozempic often find that they feel satisfied with smaller portions, helping them adhere to lower-calorie diets.
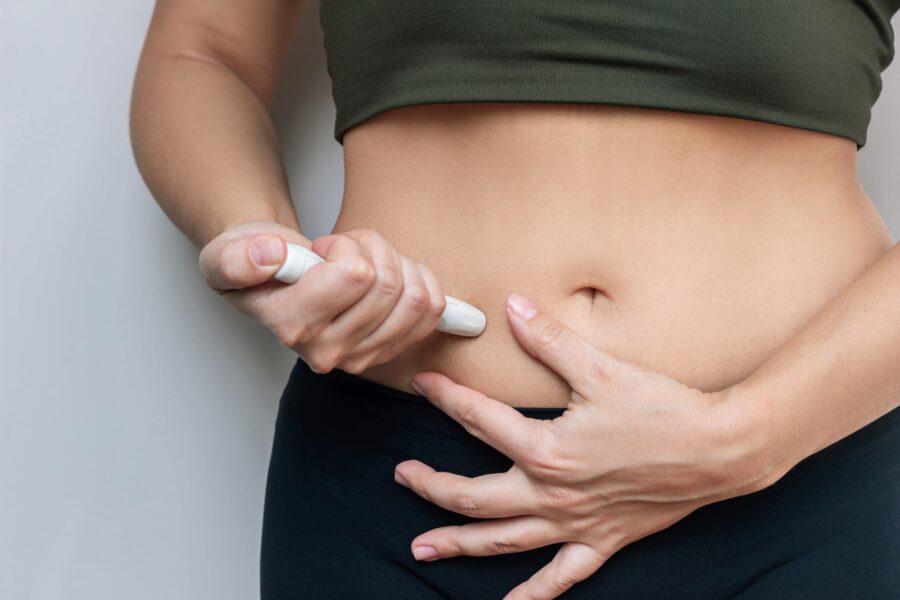
This has led to its off-label use for weight management and, more recently, its formal approval in some regions for treating obesity. It is administered as a once-weekly injection.
Some studies have shown that people who used Ozempic, along with a healthy diet and exercise, lost an average of 10-17% of their body weight over about a year. This is a big improvement compared to those who didn’t use the medication.
Another study focusing on people with type 2 diabetes, who often find it difficult to lose weight due to insulin resistance, found that Ozempic helped participants shed up to 11% of their body weight.
Today, Ozempic protocols are being used as an alternative to bariatric surgery to help control obesity. In multiple studies, Ozempic works best when paired with a balanced diet and regular exercise routine.
The consensus in the medical community is that Ozempic is generally safe and effective for managing diabetes and aiding weight loss, especially when used under the supervision of a healthcare professional, such as a metabolic doctor or endocrinologist.
However, like any medication, Ozempic comes with potential side effects and considerations.
Common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
These side effects are typically more noticeable when someone first starts the medication but tend to decrease as the body adjusts over time. For many people, these symptoms are mild and manageable.
There are also some rarer side effects, such as an increased risk of gallstones or thyroid problems. If you have a personal or family history of thyroid disease, it’s important to discuss these risks with your doctor before starting Ozempic.
It’s also worth noting that Ozempic can lower blood sugar levels, which is great for those with diabetes. However, for individuals using Ozempic solely for weight loss, this could lead to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) if combined with other medications or fasting diets.
That's why it’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider when using Ozempic for weight loss.
Cost
Since Ozempic is relatively new and lacks FDA-approved generic alternatives, its cost can be a significant barrier for many individuals. With an average price of approximately $1,200 per month, access to the medication may be limited for those without insurance coverage or financial assistance.
This can make it difficult for people who could benefit from Ozempic, particularly in long-term weight management.
Obesity is increasingly being recognized as a disease rooted in biology, not just lifestyle choices. If weight gain were entirely controllable by diet and exercise alone for obese individuals, then obesity would not be classified as a disease.
However, for many people, weight management involves complex metabolic and neurological factors. This is why many who stop taking medications like Ozempic often regain the lost weight, as the underlying causes of obesity, such as hunger signals and energy regulation, remain unresolved.
Obesity is not just about willpower or temporary solutions—it’s a chronic condition that requires ongoing management, much like diabetes or hypertension. It is tied to dysfunctions in the brain’s neural circuitry, particularly in the pathways that regulate appetite and satiety.
These pathways can be influenced by genetics, environment, and even early life experiences.
Ozempic is generally prescribed to individuals who are either overweight or obese and have struggled to lose weight through lifestyle changes alone.
It is also an option for people who may have health conditions related to their weight, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol. In these cases, the medication can serve as an additional tool to help reduce the health risks associated with excess weight.
However, it’s essential to remember that Ozempic is not a substitute for a healthy lifestyle. Anyone considering this medication should use it alongside ongoing efforts to improve nutrition, increase physical activity, and create sustainable lifestyle habits.
Fitness and healthy eating remain the foundation for long-term health, and Ozempic is meant to supplement, not replace, these efforts.
Delaying aging with Ozempic
A 2024 study suggests that Ozempic may do more than help with weight loss—it could also slow down the aging process by reducing the risk of death from various causes, including heart disease.
The key ingredient in Ozempic, semaglutide, has been found to lower inflammation, boost heart health, and improve how the body handles energy and metabolism. These benefits not only help you feel better right now but may also reduce some of the factors that speed up aging, such as oxidative stress and chronic inflammation.
While more research is needed, Ozempic’s ability to improve these critical functions shows promise as a potential longevity drug in the future.
Research suggests that Ozempic may help preserve cognitive function by improving insulin sensitivity and lowering blood sugar levels. This is significant because high blood sugar and insulin resistance have been linked to cognitive decline and diseases like Alzheimer’s, often called "Type 3 diabetes."
By controlling blood sugar and reducing oxidative stress, Ozempic could offer protective benefits for the brain, potentially slowing down cognitive aging and reducing the risk of memory-related conditions.
Here’s plan for women that will help you stay in shape while using Ozempic:
And for men:
While Ozempic shows promise as a weight loss aid and even offers potential health benefits like improved metabolic function and cognitive protection, it’s important to remember that it’s not a magic solution.
Sustainable weight management still hinges on the foundation of regular exercise, a balanced diet, and a healthy lifestyle. Medications like Ozempic can be helpful tools for those struggling with weight loss, but they should always be seen as part of a broader commitment to long-term fitness and well-being.