The Five Key Supplements You Need to Build Muscles
30 years ago, gaining muscle was relatively uncomplicated. You put in a ton of effort at the gym, drank your milk, ate your steak, and slept a lot. Now, it appears that just knowing what to put in your body to make it grow requires a degree in chemistry.
Bodybuilding supplements have grown into a billion-dollar industry. We've been persuaded by cunning marketers that we must pay a sizable sum each month in order to even have a chance at gaining muscle.
In this article, we smash through all of that marketing hype to reveal the truth about what supplements you really need to build a massive, lean physique.
Today, there is a ridiculous amount of emphasis placed on the role of supplementation in building muscle. A lot of guys believe that if they can’t afford to spend $100 or more per month on supplements, then there’s no point working out.
What they fail to realize is that supplements are exactly that – supplements to working out and eating properly. At best, they will provide you with an extra 10 to 20% in terms of gains. So, unless you’re working out intensely and smartly while also eating for muscle gain, you’ll get absolutely nothing out of supplementation.
So before you even consider buying supplements, make sure that you know what you’re doing in the gym and that when you are on the gym floor your focus like a laser beam on the muscle that you’re working, finding the exercises that actually work and using a rep range that varies from extremely high (i.e. 50) to extremely low (i.e. 4 – 6).
In terms of nutrition, you should be eating 5 to 6 times per day, making sure to get lean protein complex carbs and healthy fats and at every meal. You will also be wanting to create a daily caloric excess of around 500 calories.
- Protein powder – Whey isolates, and hydrolyzed whey, egg protein powder, soy protein, milk protein, beef protein, casein protein, and plant protein powder.
- L-Leucine
- Glutamine
- Nitric Oxide enhancers – Arginine, Citrulline
- Creatine Monohydrate
Protein is the key nutrient for building muscle. Getting it in the form of a powder makes it easy to fast-acting amino acids into your system to rebuild the muscle tissue that has been damaged by your workout.
Here are ten things to consider when shopping for protein powder:
- You need a protein powder that delivers about 130 cal per scoop.
- Your protein powder should be low in fats, carbohydrates and sugars.
- It should provide you with at least 20 g of protein per scoop.
- You don’t want lots of chemical sounding ingredients listed under the nutrition facts.
- Try to get a protein powder that uses stevia rather than an artificial sweetener.
- Check the reviews on the mixability of the product, especially if you plan to be using a blender bottle.
- Look at reviews for the taste: if you hate the taste you are not going to drink the product.
- You do not want a product that contains artificial flavorings or sweeteners.
- Always keep in mind the purpose for which you are buying the protein powder and be sure to match the type to the function. For example, if you are trying to boost HGH levels, then you will want a casein protein product that you can take at night. If you are lactose intolerant, go for a whey isolate that has the lactose removed.
- When comparing protein powders, divide the protein grams per serving by the individual serving size in grams. Ideally you should have a product that is 80% protein by weight. If not, put it back and keep searching.
Leucine - this amino acid is one of the three BCAA’s, along with isoleucine and valine. It alone, however, has the ability to stimulate muscle protein synthesis. As such, it is the most important amino acid in your body. Leucine activates an anabolic pathway called the mTOR pathway. This pathway directly stimulates muscle protein synthesis.
If you want to stay in positive nitrogen balance (believe me, you do!), then you need to supplement with Leucine. The recommended dose is 5 to 10 g per day.
Glutamine is an amino acid which has the power to prevent muscle catabolism. It also boosts the immune system, protects against free radical damage and increases glycogen storage in the muscle cell. It is the most abundant single amino acid in your body, making up about 61% of the free intracellular amino acid pool. It contributes to protein synthesis and helps with the release of HGH from the pituitary gland.
When you work out, your body’s glutamine stores are severely depleted. If it is not replaced, this can quickly put you into a catabolic state. That is why supplementing with glutamine will help to prevent muscle wastage. Look to take in 5 to 10 g of glutamine daily
A workout program you should check:
Nitric oxide (NO) is a gas that occurs naturally inside of your body. It results when your body breaks down the amino acid arginine. NO is the body’s muscle cell signaling molecule. It regulates such processes as blood flow, oxygen release, glucose uptake, muscle velocity and muscle growth. The more nitric oxide you have in your body the faster the blood will flow, bringing more oxygen nutrients, hormones and chemicals to the muscle cell.
The effect of the increased blood flow to your muscles that results from more nitric oxide being in your system, leads to the well-known pump effect that so many desire when working out. The increased blood flow also brings more oxygen and nutrients to boost endurance.
You cannot take nitric oxide. But you can take arginine, which is the amino acid that breaks down into nitric oxide. The recommended daily dosage is 15 grams, broken up into three servings of 5 grams each, spread throughout the day. The first serving should be taken directly before your workout, with the last just before you go to bed on an empty stomach.
Research has shown that taking arginine before or after your workout does not boost HGH levels. Taken at night, however, it will stimulate growth hormone release. Arginine has also been shown to help promote sleep, which is critical to workout recovery.
It has been shown that the amino acid citrulline can enhance the nitric oxide boosting effects of arginine. That is why you will often find these two ingredients combined in a nitric oxide booster. The best ratio is 2:1 in favor of arginine.
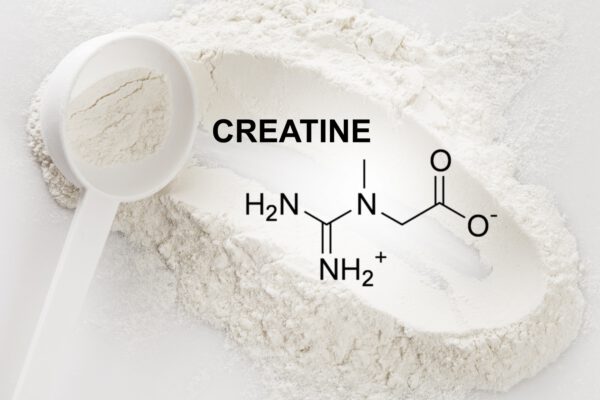
Creatine Monohydrate is the most researched sport supplement of all time. It is extremely popular and for good reason. By helping to replenish the ATP system, creatine can supply you with an instant energy burst to power your muscles to push out those last vital reps that you otherwise could not achieve. This supplement has been proven in many studies to be able to increase muscle strength and size, while also enhancing power and overall athletic ability.
There is debate whether you need to load creatine into the system when you first start taking it. The consensus seems to be that you do. This involves a loading phase where you take 5 grams 4 to 6 times throughout the day for the first week. This has been shown to boost your body’s creatine levels by around 40% in seven days. After a week you then drop back to taking 5 grams once per day. It is a good idea to take your creatine with either apple juice or grape juice as this will cause a spike in your insulin levels to allow the creatine to more readily enter the bloodstream.
You now know what supplements you need to take in order to maximize your muscle growth. Even though we have pared down to the essentials and bypassed most of the hyped up expensive products that you don’t even need, we are still left with five products. Some of them you’ll be able to combine in different complexes.
Because supplements like creatine, glutamine and leucine are stored up in the muscles, you should take them on your non training days as well as your workout days.
If your budget doesn’t stretch to everything on our list, focus on a quality whey protein and add in some creatine, and you will have most of your bases covered. Train like your life depends on it, eat 5 to 6 quality meals per day, and you will get the muscle that you’re looking for.
Frequently Asked Questions
The key supplements for muscle building include protein powder, L-Leucine, Glutamine, Nitric Oxide enhancers, and Creatine Monohydrate. These supplements can help enhance your workout results when combined with proper nutrition and exercise.
Supplements can provide an extra boost of 10-20% in muscle gains, but they are not a substitute for a solid workout and nutrition plan. Focus on intense, smart training and a balanced diet to maximize results.
Yes, you can build muscle without supplements by maintaining a consistent workout routine and eating a balanced diet rich in lean proteins, complex carbs, and healthy fats. Supplements are just an addition to enhance your progress.
Choose a protein powder that provides about 130 calories per scoop and contains fast-acting amino acids. Options include whey isolates, egg, soy, milk, beef, casein, and plant protein powders. Learn more about whey protein benefits.
Creatine Monohydrate helps increase muscle mass, strength, and exercise performance by boosting energy production in muscle cells. It is one of the most researched and effective supplements for muscle growth. Discover more about creatine benefits.
No, you don't need to spend a lot on supplements to see muscle gains. Focus on a well-rounded diet and effective workout routine first. Supplements can be a helpful addition, but they are not a necessity for everyone.